2021
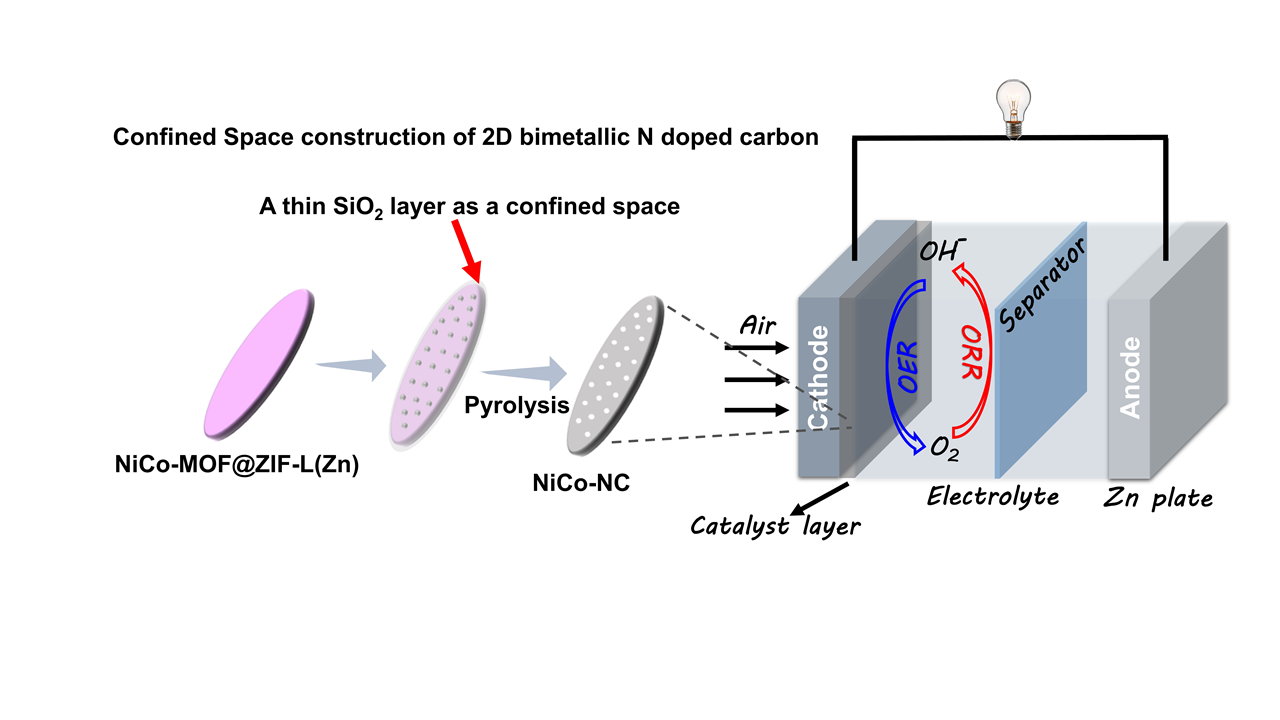
119.Wang.F.;Xu.Y.;Wang.Y.;Liang.Z.;Zhang.H.;Zhang.W.;Cao.R.;Zheng.*H.;Space-confined construction of two-dimensional nitrogen-doped carbon with encapsulated bimetallic nanoparticles as oxygen electrocatalysts,Chem. Commun., 2021, 57, 8190–8193.
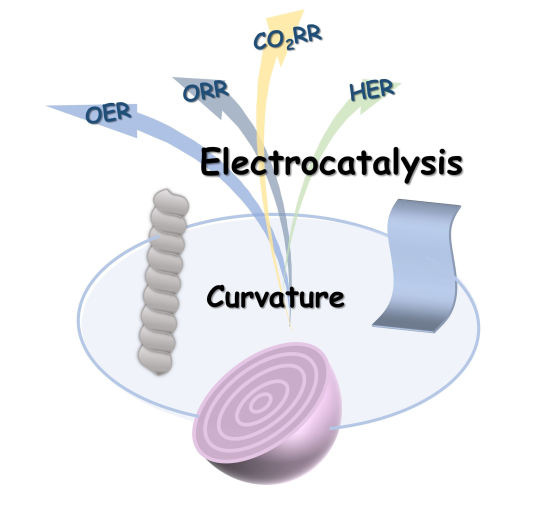
118.Wang.Y.;Bao.Z.;Shi.M.;Liang.Z.;Cao.R.;Zheng.H.*;The Role of Surface Curvature in Electrocatalysts,Chem.Eur.J.2022,28,e202102915.
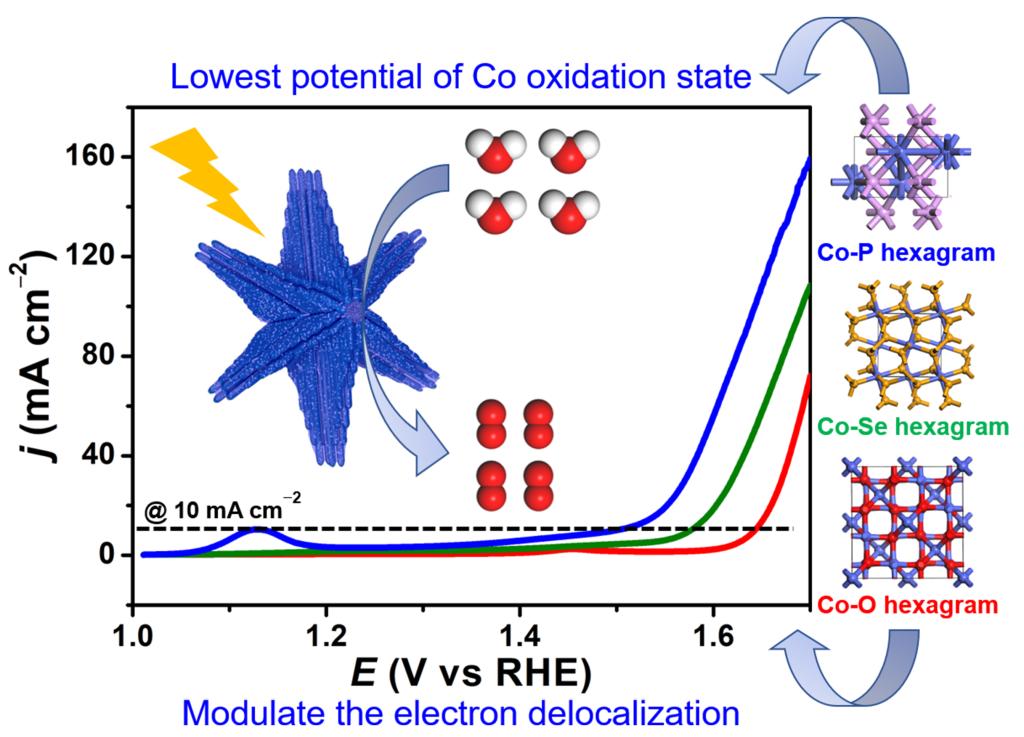
117.Liang.Z.;Yang.C.;Zhang.W.;Zheng.H.*;Cao.R.*;Anion engineering of hierarchical Co-A (A = O, Se, P) hexagrams for efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction,Chinese Chem. Lett.,2021,32,3241–3244

116.Gao.X.;Yang.S.;Zhang.W.;Cao.R.; Biomimicking Hydrogen-Bonding Network by Ammoniated and Hydrated Manganese (Ⅱ) Phosphate for Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation. Acta Phys. -Chim. Sin., 2021, 37, 2007031.
115.Chen.Y.;Yang.S.;Liu.H.;Zhang.W.*;Cao.R.*;An unusual network of α-MnO2 nanowires with structure-induced hydrophilicity and conductivity for improved electrocatalysis.Chinese J. Catal.,2021,42,1724–1731

114.Yang.S.;Wan.S.;Shang.F.;Chen.D.;Zhang.W.*;Cao.R.*; Autologous manganese phosphates with different Mn sites for electrocatalytic water oxidation. Chem. Commun., 2021, 57, 6165-6168.
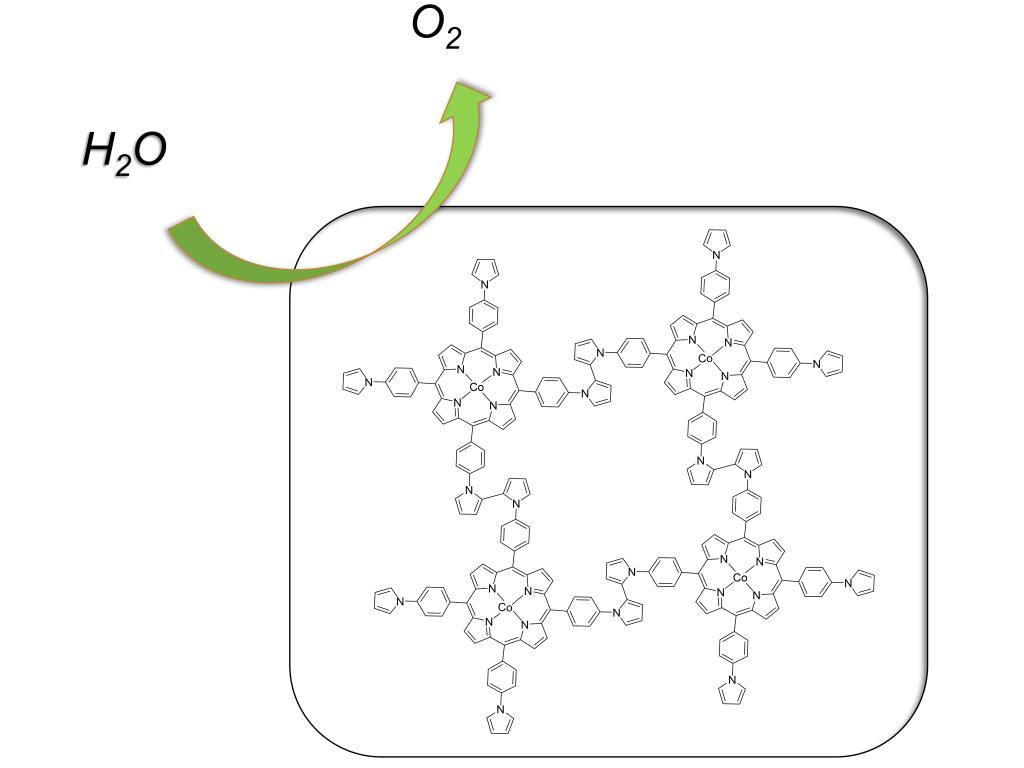
113.Zhang,Q.;Wang,Y.;Wang,Y.;Yang,S.;Wu,X.;Lv,B.;Wang,N.;Gao,Y.;Xu,X.;Lei,H.*;Cao.R.*;Electropolymerization of cobalt porphyrins and corroles for the oxygen evolution reaction,Chinese Chem Lett,2021,32,3807–3810.
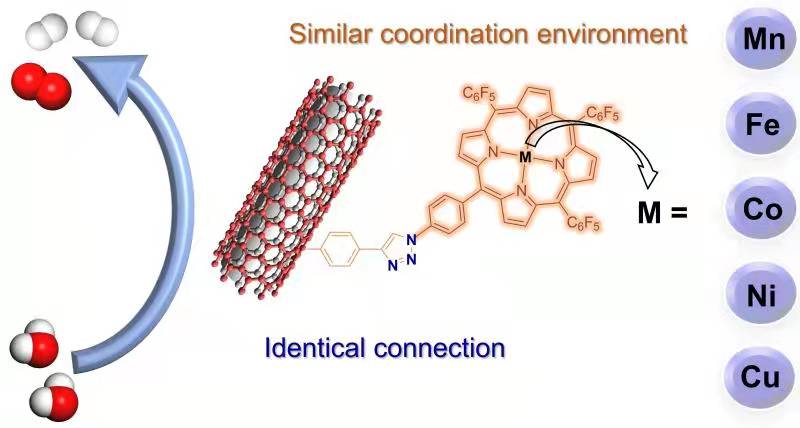
112.Jin,X.;Li,X.;Lei,H.;Guo,K.;Lv,B.;Chen,D.;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*;Comparing electrocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution activities of first-row transition metal complexes with similar coordination environments.J. Energ. Chem,2021,63,659-666.
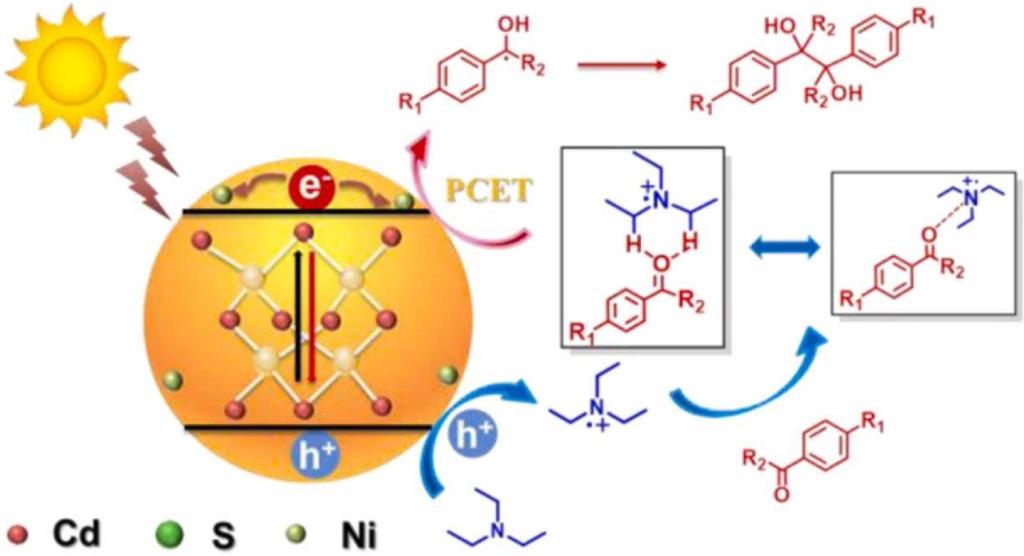
111.Hu,R.;Xie,W-H.;Wang,H-Y.*;Guo,X-A.;Zhang,X-P.*;Cao.R.*;Visible light-driven carbon-carbon reductive coupling of aromatic ketones activated by Ni-doped CdS quantum dots: An insight into the mechanism.Appl Catal B: Environ,2022,304,120946.
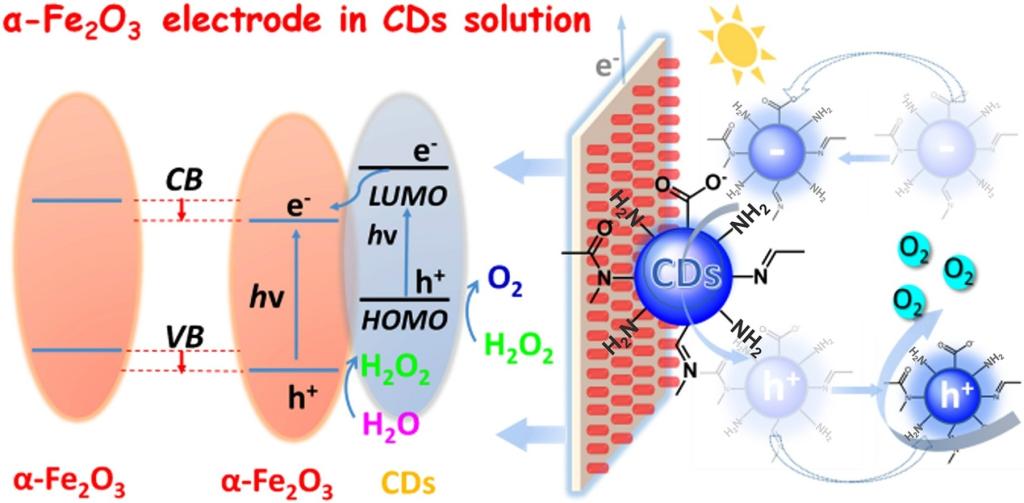
110.Wang,H-Y,;Hu,R.;Wang,N.;Hu,G-L.;Wang,K.;Xie,W-H.;Cao,R.;Boosting photoanodic activity for water splitting in carbon dots aqueous solution without any traditional supporting electrolyte.Appl Catal B: Environ,2021,296,120378.
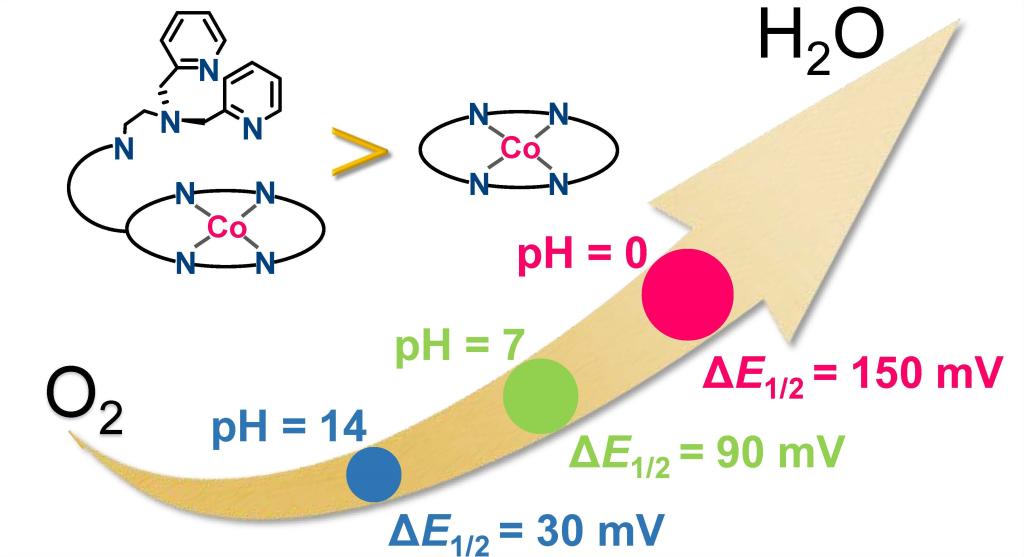
109.Han,J.;Wang,N.;Li,X.*;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*;Improving Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Activity and Selectivity with a Cobalt Corrole Appended with Multiple Positively Charged Proton Relay Sites,J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 45, 24805–24813.
108.Lv,H.;Guo,H.;Guo,K.;Lei,H.;Zhang,W.;Zheng,H.;Liang,Z.*;Cao,R.*;Substituent position effect of Co porphyrin on oxygen electrocatalysis. Chin. Chem. Lett., 2021, 32, 2841-2845.
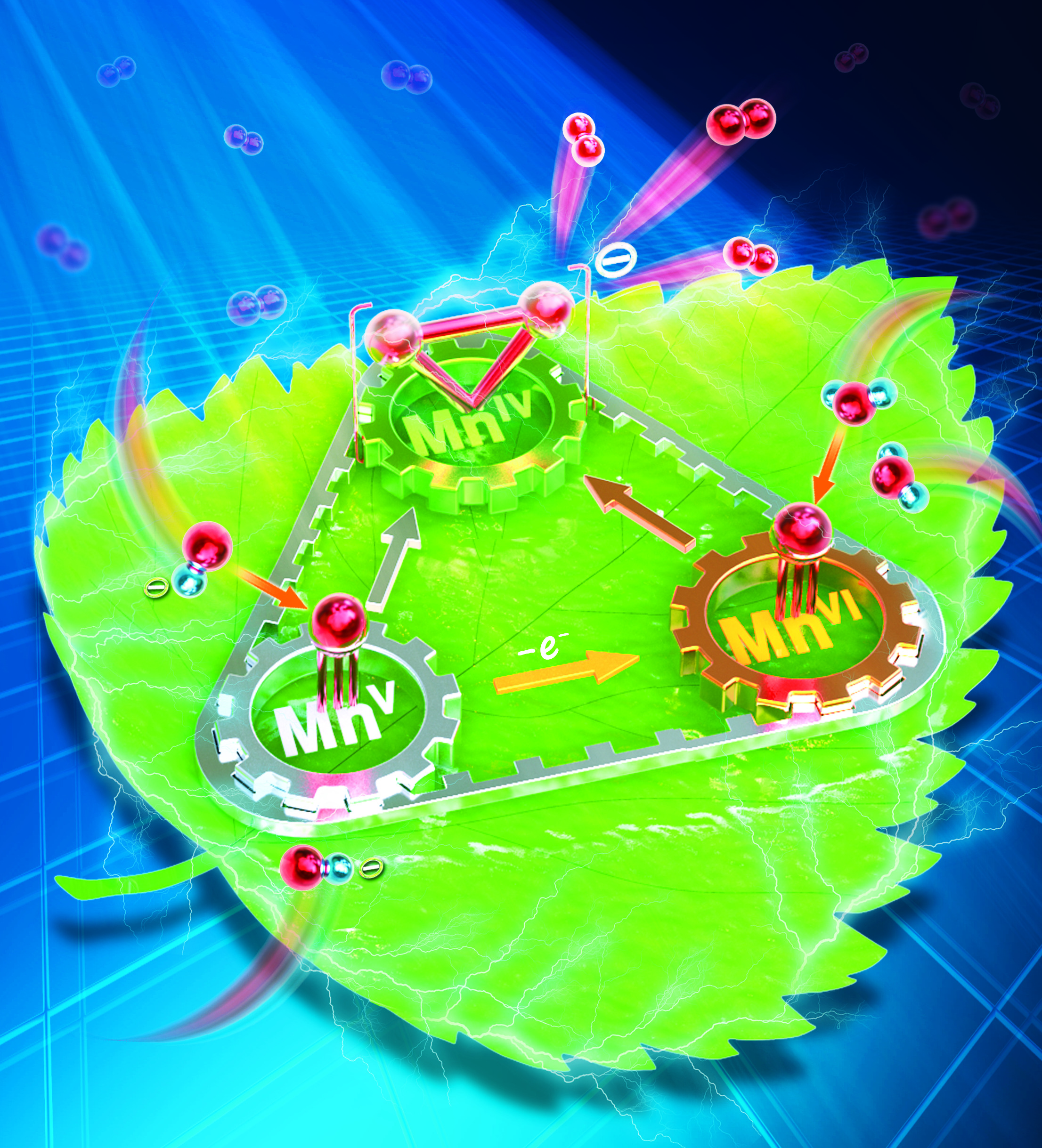
107.Li,X.;Zhang,X-P.;Guo,M.;Zhang,W.; Lee,Y-W.*; Nam,Wonwoo.*;Cao,R.*,Identifying Intermediates in Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation with a Manganese Corrole Complex.J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2021,143,14613–14621.

106.Zhang,W.;Cao,R*,Switching the O–O bond-formation mechanism by controlling water activity.Chem,2021,7,1981–1992.
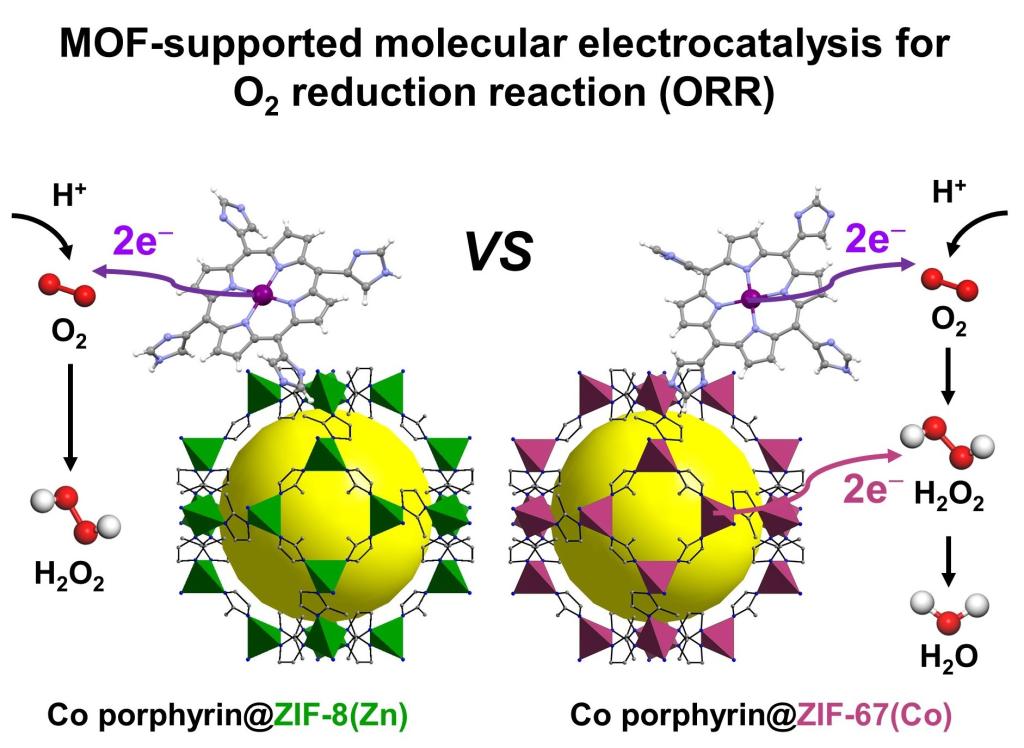
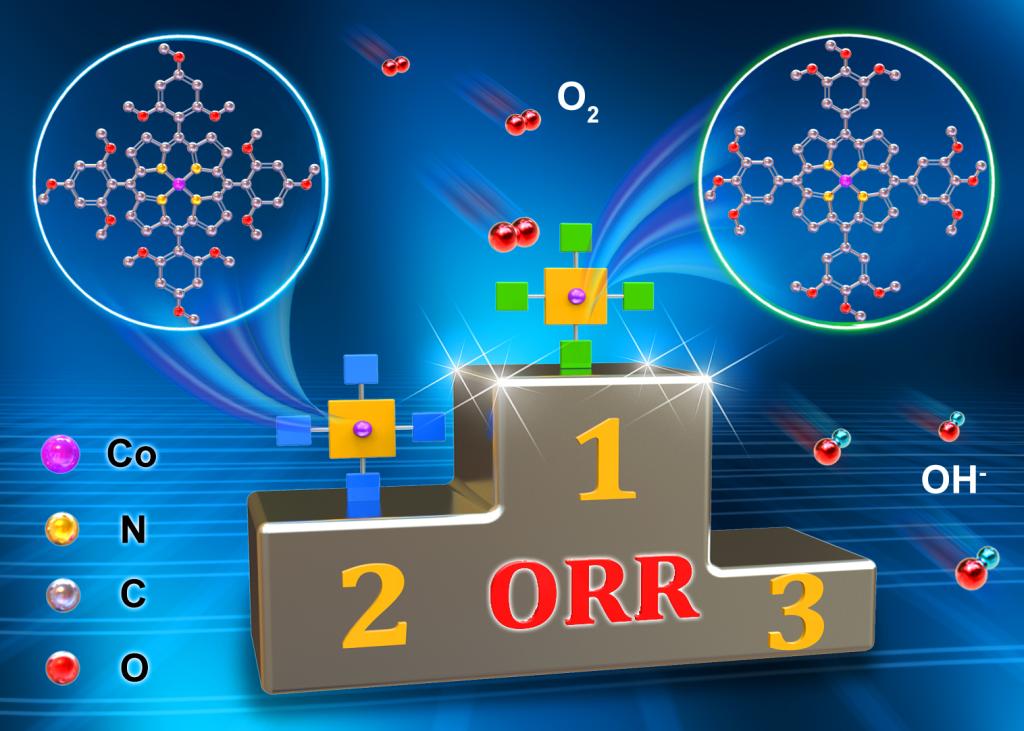
105.Liang,Z.;Guo,H.;Zhou,G.;Guo,K.;Wang,B.;Lei,H.;Zhang,W.;Zheng,H.;Apfel Ulf-Peter.;Cao,R.*; Metal–Organic-Framework-Supported Molecular Electrocatalysis for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 8472–8476.[Highly Cited Paper]
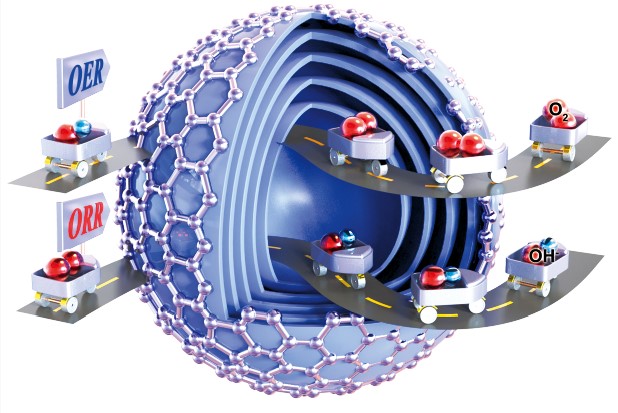
104.Liang,Z.;Kong,N.;Yang,C.;Zhang,W.;Zheng,H.*;Lin,H.*;Cao,R.*; Highly Curved Nanostructure-Coated Co, N-Doped Carbon Materials for Oxygen Electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 12759–12764.[Highly Cited Paper]
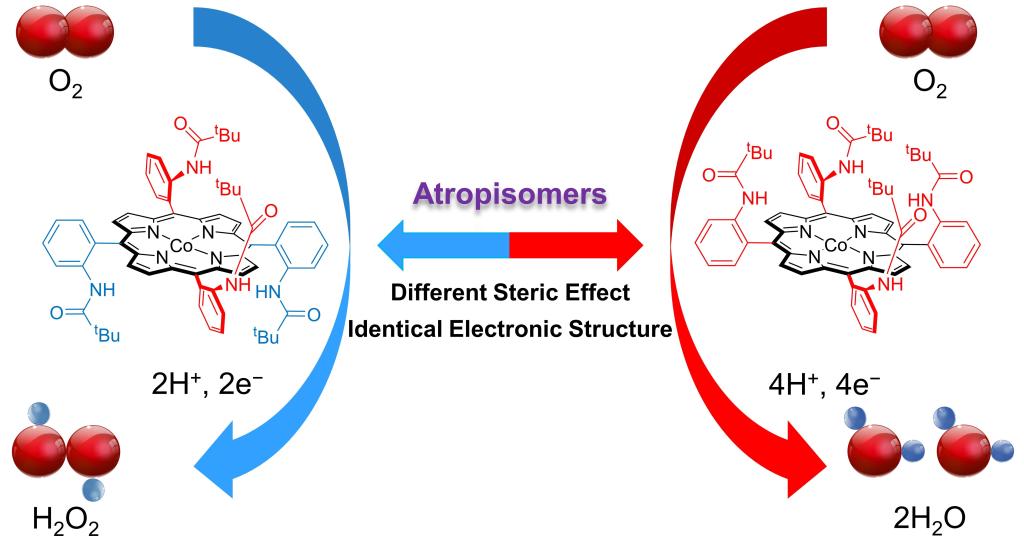
103.Lv,B.;Li,X.;Zhang,W.;Apfel,Ulf-peter.;Cao,R.*,Controlling Oxygen Reduction Selectivity through Steric Effects: Electrocatalytic Two-Electron and Four-Electron Oxygen Reduction with Cobalt Porphyrin Atropisomers,Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.2021,60,12742 –12746.
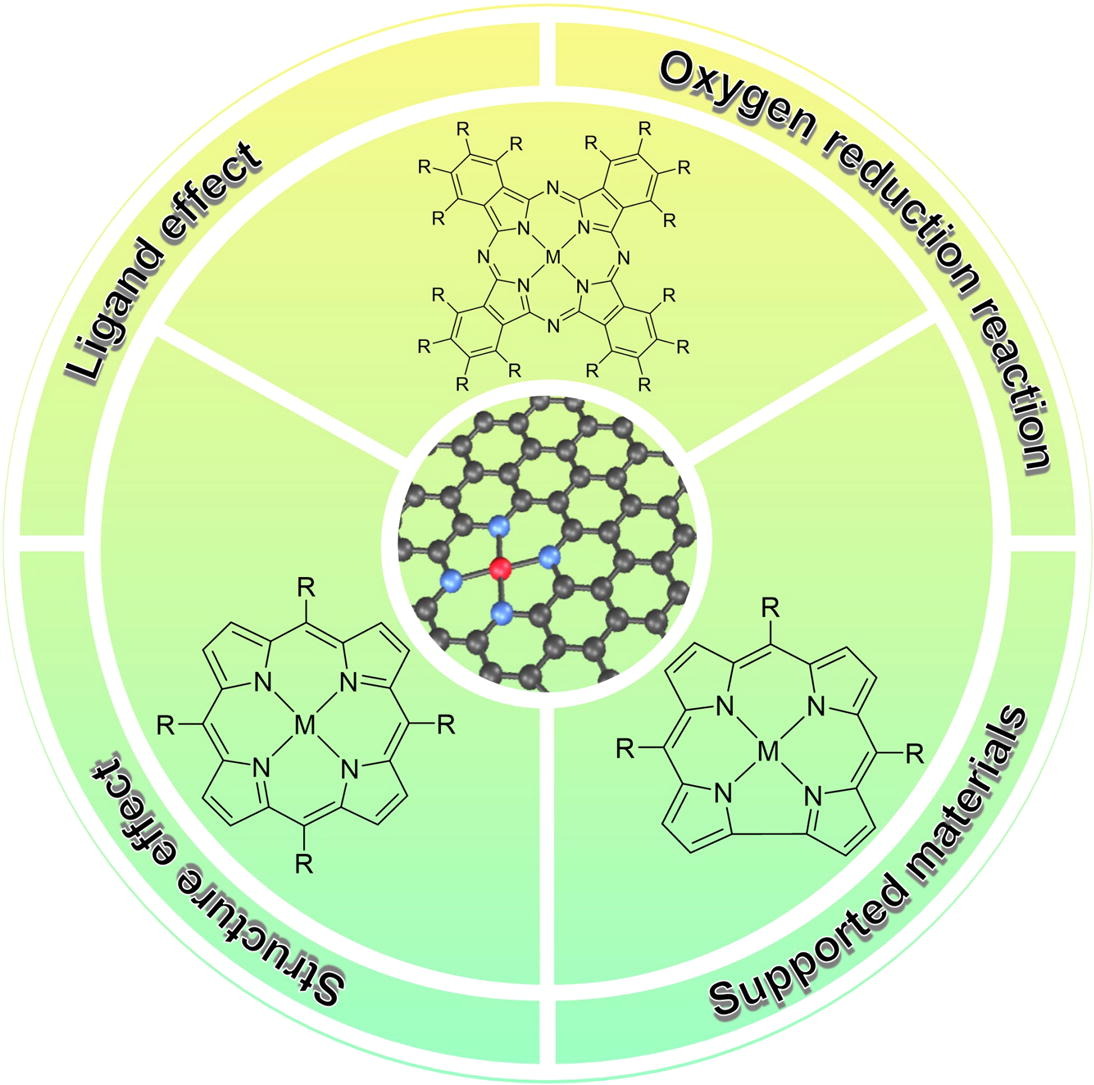
102.Li,Y.;Wang,N.;Lei,H.*;Li,X.;Zheng,H.;Wang,H.;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*,Bioinspired N4-metallomacrocycles for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction. Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 442, 213996.

101.Guo,K.;Lei,H.;Li,X.;Zhang,Z.;Wang,Y.;Guo.H.;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*,Alkali metal cation effects on electrocatalytic CO2 reduction with iron porphyrins. Chin. J. Catal., 2021, 42, 1439-1444.

100.Lei,H.;Zhang,Q.;Wang,Y.;Gao,Y.;Wang,Y.;Liang,Z.;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*,Significantly boosted oxygen electrocatalysis with cooperation between cobalt and iron porphyrins.Dalton Trans., 2021, 50, 5120–5123.

99.Zhang,X.;Wang,H.;Zheng,H.;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*; O–O bond formation mechanisms during the oxygen evolution reaction over synthetic molecular catalysts. Chin. J. Catal., 2021, 42, 1253-1268.[Highly Cited Paper]
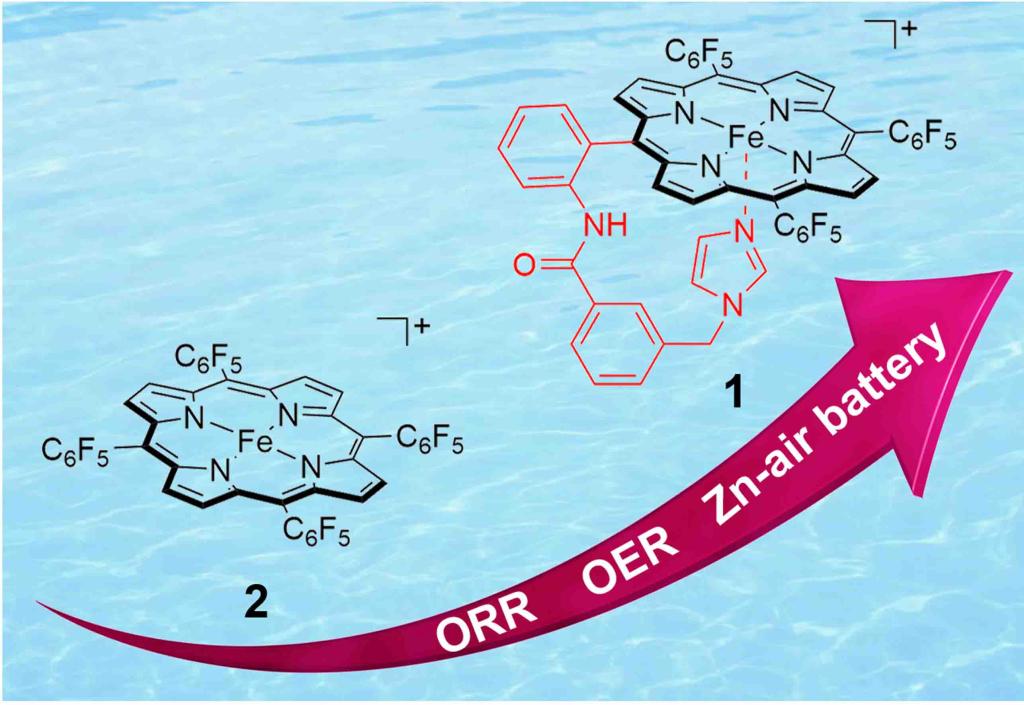
98.Xie,L.;Zhang,X.;Zhao,B.;Li,Ping.;Qi,J.;Guo,X.;Wang,B.;Lei,H.;Zhang,W.;Ulf-Peter Apfel.;Cao,R.*; Enzyme-Inspired Iron Porphyrins for Improved Electrocatalytic. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 7576–7581.[Highly Cited Paper]
97.Zhang,X.;Anirban Chandra.;Lee,Y.;Cao,R.*;Kallol Ray.*;Wonwoo Nam.*; Transition metal-mediated O–O bond formation. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 4804–4811.[Highly Cited Paper]

96.Liang,Z.;Wang,H.;Zheng,H.;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*; Porphyrin-based frameworks for oxygen electrocatalysis and catalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 2540-2581.[Highly Cited Paper]
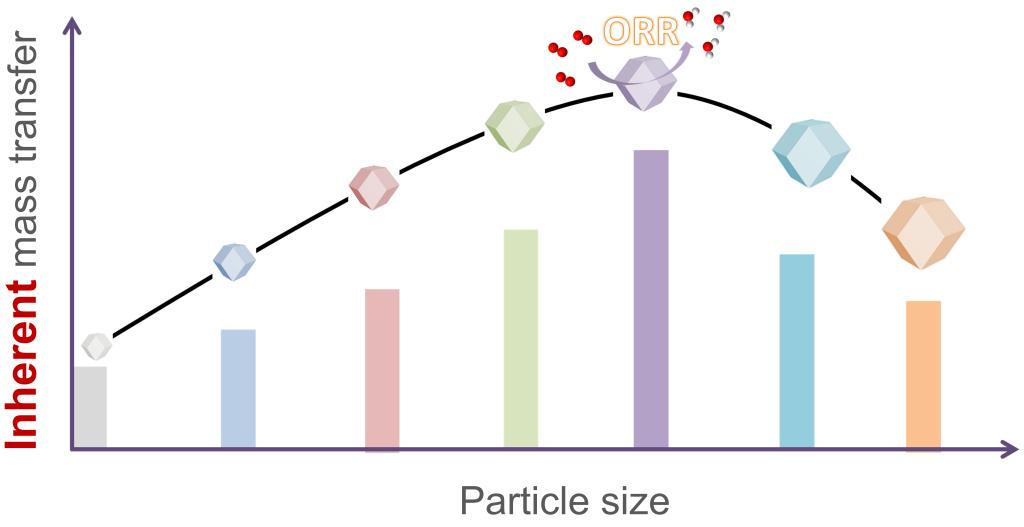
95.Wang,Y.;Wang,B.*;Yuan,H.;Liang,Z.;Huang,Z.;Zhou,Y.;Zhang,W.;Zheng,H.*;Cao,R.*,Inherent mass transfer engineering of a Co, N co-doped carbon material towards oxygen reduction reaction.J. Energy Chem., 2021, 58, 391–396.
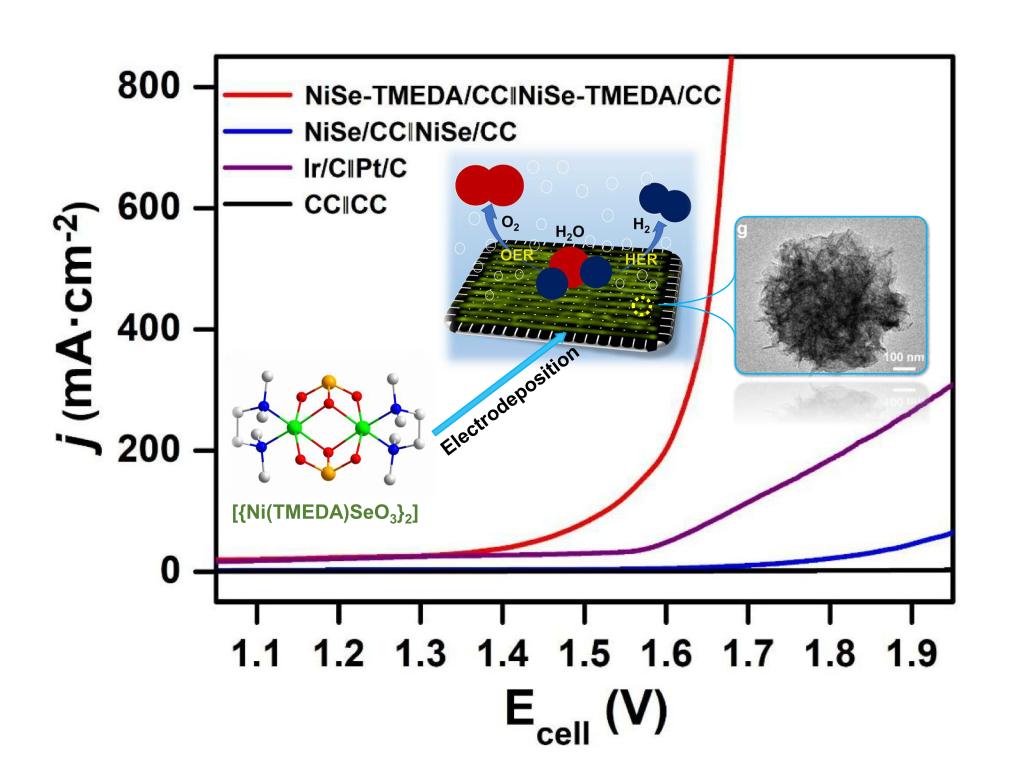
94.Chen,D.;Chen,Y.;Zhang,W.*;Cao,R.*, Nickel selenide from single-molecule electrodeposition for efficient electrocatalytic overall water splitting.New J. Chem., 2021,45, 351-357.
93.Qin,H.;Wang,Y.;Wang,B.*;Duan,X.;Lei,H.;Zhang,X.;Zheng,H.;Zhang,W.;Cao,R.*; Cobalt porphyrins supported on carbon nanotubes as model catalysts of metal-N4/C sites for oxygen electrocatalysis. J. Energy Chem., 2021, 53, 77-81.[Highly Cited Paper]
首页上页1下页尾页